Prime Minister Vs President: Understanding The Key Differences And Roles
The debate between the roles of a Prime Minister and a President is significant in understanding the political landscape of various countries. These two positions command different powers and responsibilities, depending on the governmental structure in place. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between a Prime Minister and a President, their functions, and how they influence governance in their respective countries.
In many countries, the titles of Prime Minister and President are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. However, it is essential to recognize that these roles can differ significantly based on the political system, such as parliamentary or presidential systems. This article aims to clarify these differences and provide insights into how each role operates within its political framework.
Furthermore, understanding the differences between these two roles is crucial, especially for those interested in political science, governance, or international relations. By delving into their functions, powers, and responsibilities, we can gain a clearer picture of global politics and governance.
- Unveiling The Mystery Of Masa49 A Deep Dive
- Fleetwood Mac Band Members Dead The Untold Stories Behind The Legends
Table of Contents
- Biography of Prime Ministers and Presidents
- Key Differences Between Prime Minister and President
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Methods of Election
- Powers and Authority
- Accountability and Governance
- Examples from Around the World
- Conclusion
Biography of Prime Ministers and Presidents
Both Prime Ministers and Presidents have unique biographical backgrounds that shape their political ideologies and leadership styles. Here’s a brief overview of their roles:
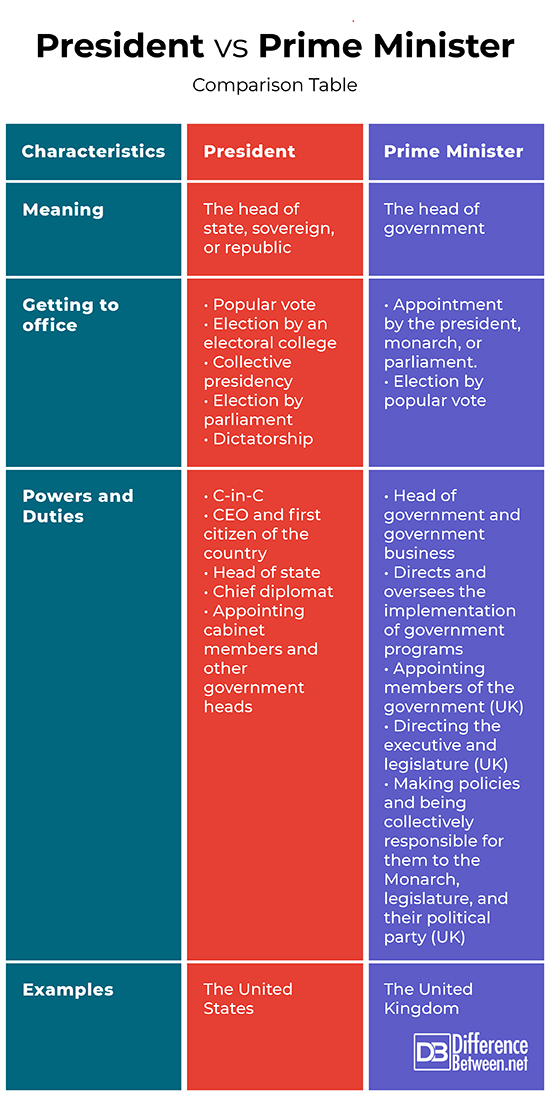
Prime Ministers typically emerge from the parliamentary system, representing a political party in the legislature. They are often seen as the head of the government and are responsible for executing laws and policies. In contrast, Presidents often serve as both the head of state and the head of government in presidential systems, having distinct powers that affect national governance.
| Role | Prime Minister | President |
|---|---|---|
| Head of Government | Yes | Yes |
| Head of State | No | Yes |
| Election Method | Parliamentary vote | Popular vote or electoral college |
| Tenure | Varies by country | Fixed term |
Key Differences Between Prime Minister and President
The primary difference between a Prime Minister and a President lies in their method of selection and the powers they wield.
- Mp4moviez In Your Ultimate Guide To Downloading Movies Legally And Safely
- Hdhub4uspa Your Ultimate Destination For Highquality Content
1. Method of Selection
- Prime Minister: Elected by the parliament; their position depends on maintaining the confidence of the legislature.
- President: Elected by the populace or an electoral college, often serving a fixed term.
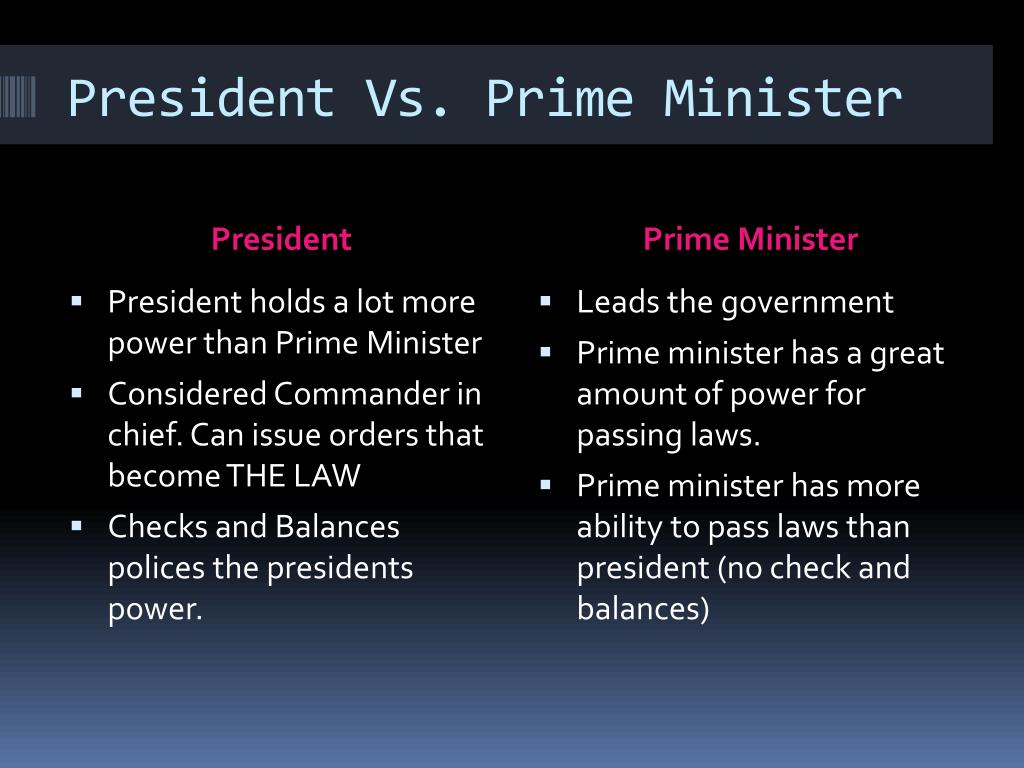
2. Powers and Responsibilities
- Prime Minister: Generally holds limited powers but has significant influence over the legislative process.
- President: Often has extensive powers, including veto authority, military command, and diplomatic roles.
Roles and Responsibilities
The roles of Prime Ministers and Presidents differ significantly based on their governmental frameworks.
Prime Ministerial Roles
- Leads the executive branch of government.
- Represents the government in parliament.
- Responsible for domestic and foreign policies.
Presidential Roles
- Serves as the ceremonial head of state.
- Oversees the executive branch and enforces laws.
- Engages in international diplomacy and treaties.
Methods of Election
The election processes for Prime Ministers and Presidents are often governed by the constitutional framework of their countries.
Prime Minister Election Process
- Typically arises from a parliamentary election.
- Must maintain the support of the majority party or coalition.
Presidential Election Process
- Involves a direct or indirect vote by the populace.
- May require a majority or electoral college vote for victory.
Powers and Authority
The powers of Prime Ministers and Presidents can vary widely, impacting their governance styles.
Prime Ministerial Powers
- Legislative powers through majority control.
- Appointment of cabinet members and government officials.
- Influence over national policies and budgets.
Presidential Powers
- Veto power over legislation.
- Commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
- Authority to negotiate and sign treaties.
Accountability and Governance
Accountability varies significantly between Prime Ministers and Presidents, affecting how they interact with the legislature and the electorate.
Accountability of Prime Ministers
- Must maintain support from parliament to remain in office.
- Can face votes of no confidence.
Accountability of Presidents
- Accountable to the public through elections.
- Impeachment processes exist for misconduct.
Examples from Around the World
To illustrate the differences between Prime Ministers and Presidents, let’s look at examples from various countries.
Prime Minister Example: United Kingdom
The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government and is elected by the House of Commons. The Prime Minister's powers include setting government policy and representing the UK internationally.
Presidential Example: United States
The President of the United States serves as both the head of state and head of government, elected through a nationwide electoral process. The President has significant powers over domestic and foreign policies, making them a pivotal figure in American governance.
Conclusion
In summary, the roles of Prime Ministers and Presidents are distinct yet crucial to the functioning of their respective governments. Understanding the differences in their powers, responsibilities, and methods of election is vital for anyone interested in political science and governance. We encourage readers to share their thoughts on this topic and engage in discussions about global governance.
For more information on political systems and governance, feel free to explore other articles on our site. Your engagement and insights are always welcome!
- Movierulz 5 Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Movies In 2023
- Amazon Prime Show About Virtual Reality Your Ultimate Guide To The Future Of Entertainment
Difference Between President and Prime Minister Difference Between
PPT Constitutional Monarchy vs. Democracy PowerPoint Presentation

Prime Minister vs. President List of Key Differences YourDictionary