Unraveling The Mysteries Of The Corticopontocerebellar Tract: A Journey Through The Brain's Hidden Pathways
Let’s dive into something that’s as fascinating as it is complex: the corticopontocerebellar tract. Now, if you’re scratching your head wondering what that even means, don’t worry—you’re not alone. This tract is like a hidden highway in your brain that connects different regions, allowing them to communicate and work together. Think of it as the secret messenger that keeps your movements smooth and your coordination on point. So, whether you’re juggling a ball, typing on your keyboard, or even just walking, this tract is playing a crucial role behind the scenes.
But here’s the thing: the corticopontocerebellar tract isn’t just about movement. It’s also involved in fine-tuning your motor skills, ensuring that your body responds precisely to what your brain is telling it to do. Ever wondered why you don’t trip over every single step you take? Or why you can catch a ball without flailing around like a chicken with its head cut off? Yeah, this tract deserves a lot of credit for that.
Now, if you’re someone who’s into neuroscience, anatomy, or just curious about how the brain works, you’re in for a treat. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about the corticopontocerebellar tract in a way that’s easy to understand. No fancy jargon, no overwhelming medical terms—just straight-up knowledge that’ll make you go, “Oh, so that’s how it works!”
- Manuel Garciarulfo Movies And Tv Shows A Dive Into The World Of This Talented Actor
- Vega Moviecom Your Ultimate Destination For Cinematic Adventures
Table of Contents
- What Is the Corticopontocerebellar Tract?
- Anatomy of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
- The Function of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
- Connections and Pathways
- Why Is the Corticopontocerebellar Tract Important?
- Dysfunction of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
- Diagnosing Issues with the Tract
- Treatment Options for Tract Dysfunction
- Current Research and Discoveries
- The Future of Corticopontocerebellar Tract Research
What Is the Corticopontocerebellar Tract?
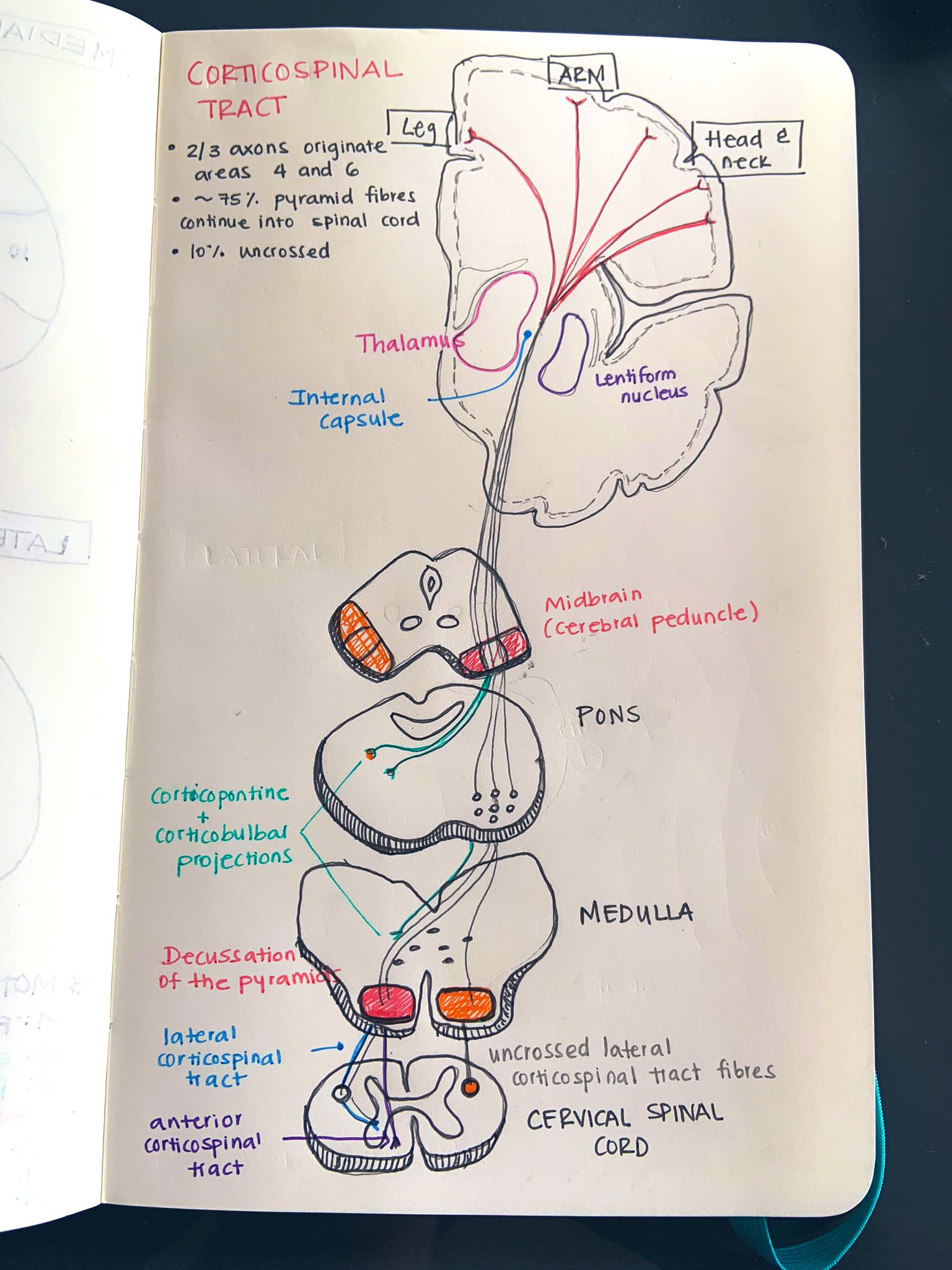
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The corticopontocerebellar tract is essentially a bundle of nerve fibers that serves as a communication line between different parts of your brain. It connects the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for higher-order functions like thinking and decision-making, to the cerebellum, which handles coordination and balance. Think of it like a bridge that links two islands, allowing traffic to flow smoothly between them.
This tract is part of a larger network in the brain called the corticopontine pathway. Its job is to send signals from the motor cortex to the pons, which then relays those signals to the cerebellum. In simpler terms, it’s the middleman that makes sure your brain and body are on the same page when it comes to movement.
Why Should You Care?
Here’s the thing: without this tract, your movements would be all over the place. Imagine trying to walk in a straight line while feeling like you’re on a boat in rough waters. Or trying to pick up a cup of coffee without spilling it everywhere. Yeah, not ideal. That’s why understanding the corticopontocerebellar tract is crucial, especially if you’re interested in how the brain controls movement.
- Desiremovies The Ultimate Destination For Movie Buffs
- Spiderman Sophie Rain Spiderman Ndash The Untold Story Of A Webswinging Sensation
Anatomy of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
Now, let’s get a little more technical. The corticopontocerebellar tract originates in the cerebral cortex, specifically in the motor and premotor areas. From there, it travels through the internal capsule, a dense bundle of nerve fibers that acts like a highway for neural signals. It then crosses over to the pons, which is located in the brainstem.
Once in the pons, the tract branches out and sends fibers to the cerebellum via the middle cerebellar peduncle. This is where the magic happens. The cerebellum takes these signals and uses them to fine-tune your motor skills, ensuring that your movements are smooth, coordinated, and accurate.
Breaking It Down
- Cerebral Cortex: The starting point of the tract, responsible for initiating movement.
- Internal Capsule: The highway that carries signals from the cortex to the pons.
- Pons: The relay station that sends signals to the cerebellum.
- Cerebellum: The destination, where signals are processed to coordinate movement.
The Function of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
So, what exactly does this tract do? Well, its primary function is to transmit motor commands from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum. This allows the cerebellum to refine those commands, making sure your movements are precise and efficient. It’s like having a personal trainer in your brain that helps you perfect your form.
But that’s not all. The corticopontocerebellar tract also plays a role in learning new motor skills. Ever noticed how awkward you feel when you first try something new, like riding a bike or playing a musical instrument? That’s because your brain is still figuring out the best way to execute those movements. Over time, the tract helps you improve, making the process smoother and more natural.
Key Functions
- Transmitting motor commands from the cortex to the cerebellum.
- Refining motor skills and ensuring coordination.
- Facilitating the learning of new motor skills.
Connections and Pathways
As we mentioned earlier, the corticopontocerebellar tract is part of a larger network in the brain. It connects to other tracts and pathways that work together to control movement. For example, it interacts with the corticospinal tract, which is responsible for voluntary movement, and the corticobulbar tract, which controls facial movements.
These connections are crucial because they allow different parts of the brain to communicate and coordinate their efforts. It’s like a team of specialists working together to achieve a common goal. Each member has its own role, but they all need to collaborate to get the job done.
Key Connections
- Corticospinal Tract: Controls voluntary movement.
- Corticobulbar Tract: Controls facial movements.
- Reticulospinal Tract: Regulates posture and balance.
Why Is the Corticopontocerebellar Tract Important?
By now, you probably have a pretty good idea of why this tract is so important. It’s the backbone of motor coordination, ensuring that your movements are smooth and precise. But its significance goes beyond just physical movement. The corticopontocerebellar tract also plays a role in cognitive functions like attention and problem-solving.
For example, studies have shown that people with damage to this tract often experience difficulties with tasks that require fine motor control, such as writing or buttoning a shirt. They may also struggle with cognitive tasks that involve planning and decision-making. This highlights just how integral the tract is to both physical and mental processes.
Real-World Implications
Understanding the importance of the corticopontocerebellar tract has real-world implications, especially in the field of medicine. For instance, doctors can use this knowledge to diagnose and treat conditions that affect movement and coordination, such as Parkinson’s disease and cerebellar ataxia.
Dysfunction of the Corticopontocerebellar Tract
Now, let’s talk about what happens when things go wrong. Dysfunctions in the corticopontocerebellar tract can lead to a variety of movement disorders, ranging from mild clumsiness to severe coordination problems. These issues can be caused by a number of factors, including trauma, stroke, or neurodegenerative diseases.
One common condition associated with tract dysfunction is cerebellar ataxia. People with this condition often experience difficulty with balance, coordination, and fine motor skills. They may also have trouble speaking clearly or swallowing properly, which can significantly impact their quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms
- Difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Problems with fine motor skills, such as writing or buttoning a shirt.
- Slurred speech or difficulty speaking clearly.
- Difficulty swallowing.
Diagnosing Issues with the Tract
Diagnosing problems with the corticopontocerebellar tract can be challenging, but there are several methods that doctors use to identify issues. One common approach is to perform a neurological examination, which involves testing the patient’s reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination. Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, may also be used to get a closer look at the brain and identify any abnormalities.
In some cases, doctors may use electrophysiological tests, such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies, to assess the function of the tract. These tests can provide valuable information about how well the tract is transmitting signals and whether there are any disruptions in the process.
Diagnostic Tools
- Neurological examination.
- Imaging studies (MRI, CT scans).
- Electrophysiological tests (EMG, nerve conduction studies).
Treatment Options for Tract Dysfunction
Treating dysfunctions in the corticopontocerebellar tract can be complex, as it often involves addressing the underlying cause of the problem. In some cases, medications may be used to manage symptoms, such as muscle relaxants to reduce spasticity or anti-seizure drugs to control tremors.
Physical therapy is another important aspect of treatment, as it can help improve coordination and strength. Occupational therapy may also be beneficial, especially for patients who have difficulty with daily activities like dressing or eating. In severe cases, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
Therapeutic Approaches
- Medications to manage symptoms.
- Physical therapy to improve coordination and strength.
- Occupational therapy to assist with daily activities.
- Surgery in severe cases.
Current Research and Discoveries
As with many areas of neuroscience, research into the corticopontocerebellar tract is ongoing. Scientists are constantly uncovering new information about how this tract works and how it can be affected by various conditions. Recent studies have focused on understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying tract dysfunction, as well as developing new treatments that target these mechanisms.
One promising area of research involves the use of stem cells to repair damaged nerve fibers in the tract. This could potentially lead to breakthroughs in treating conditions like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, which are associated with tract dysfunction.
The Future of Corticopontocerebellar Tract Research
Looking ahead, the future of corticopontocerebellar tract research is bright. Advances in technology and imaging techniques are allowing scientists to study the tract in greater detail than ever before. This, in turn, is leading to new insights into how the tract functions and how it can be affected by disease.
As our understanding of the tract continues to grow, so too will our ability to develop effective treatments for conditions that affect it. Whether it’s through innovative therapies or cutting-edge technologies, the possibilities are endless. And that’s something worth getting excited about.
What’s Next?
So, where do we go from here? Well, the next step is to keep exploring, keep experimenting, and keep pushing the boundaries of what we know. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of the corticopontocerebellar tract and improve the lives of countless individuals who are affected by its dysfunction.
Conclusion
And there you have it—a deep dive into the fascinating world of the corticopontocerebellar tract. From its anatomy and function to its role in
- Hdhub4u Your Ultimate Destination For Highquality Entertainment
- Movierulz 2 Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Movies Safely
Pyramidal Tract
Tract mansion Stock Vector Images Alamy

Human Digestive Tract Anatomy, Object, Vector, Digestive System PNG